Millimeter-wave radar (or mmWave radar) is a class of radar technology that operates in the 30 GHz to 300 GHz frequency range. This offers unique advantages in applications ranging from automotive to meteorological systems.
Table of Content
ToggleIntroduction to Millimeter-Wave Radar
Millimeter-wave (mmWave) radar operates on electromagnetic waves with wavelengths ranging from 1 millimeter to 10 millimeter (frequency range of 30-300 GHz). This radar is designed for highly accurate sensing of location, velocity, and angle with minimal interference, making it ideal for a wide array of applications.
How Does Millimeter-Wave Radar Work? Millimeter-wave radar transmits pulses of millimeter electromagnetic wave energy and analyzes the reflections it receives back from targets. Multiple antennas capture these reflected signals, allowing the system to process the time of flight of these pulses. This helps compute information such as the distance to the target, angle of arrival, and relative velocity. This capability makes millimeter-wave radar particularly effective in systems that require precise sensing of human or animal presence and behavior.
Advantages of millimeter-wave (mmWave) Radar
Researchers have extensively studied various types of sensing technologies for indoor object detection measurements, including passive infrared (PIR), optical cameras, LIDAR, Wi-Fi, and 10 GHz-to-24 GHz microwave. However, these technologies pose challenges related to inaccuracy, privacy concerns, environmental robustness, and system complexity.
-
Robustness and Accuracy:
Unlike other technologies such as optical cameras and microwave systems, mmWave radar excels in both robustness and accuracy. Camera-based systems require clear views and specific lighting conditions. The HD camera system and other technologies like Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and UWB are often used for positioning. While these systems can achieve high accuracy under controlled lab conditions, their performance can significantly degrade in real-world environments. On the other hand, mmWave radar is robust to atmospheric conditions such as dust, smoke, and fog, making it reliable in various scenarios.
-
Privacy and Intrusiveness:
Camera systems, while effective, come with inherent privacy concerns due to their intrusive nature. While research is actively exploring solutions to these privacy issues, including the use of lower resolution cameras, mmWave radar provides a superior solution without compromising privacy, as it does not rely on optical imaging for tracking human activities. This not only ensures user privacy but also simplifies system implementation.
-
Interference and System Complexity:
In indoor object detection, technologies like Wi-Fi and microwave systems can suffer from interference issues, affecting their accuracy and reliability. Moreover, systems employing machine learning (ML) methods for detection, such as decision trees, hidden Markov models, and convolutional neural networks, often face challenges when it comes to implementation on embedded systems due to their computational intensity. In contrast, mmWave radar offers minimal interference and has a relatively simple system architecture, comprising radiofrequency components, digital signal processors, and antennas, making it easier to implement and integrate into various applications.
-
Range and Spatial Resolution:
Compared to traditional microwave radar systems operating in the 10 GHz-to-24 GHz range, mmWave radar offers finer spatial resolution. This means it can provide more detailed information about detected objects within the same range. Additionally, the large bandwidth of mmWave radar technology enables access to detailed structural features of targets using broadband frequency modulation signals. This is particularly beneficial in applications requiring precise detection and characterization of objects or individuals.
Applications of Millimeter-Wave (mmWave) Radar
Millimeter-wave radar finds extensive application across different industries:
-
Automotive:
In the automotive sector, mmWave radar serves as an integral component of advanced driving assistant systems (ADAS), functioning as a multi-lane, multi-object tracking device. It provides crucial features including driving safety enhancements, collision detection capabilities, and precise parking aids. The radar’s ability to accurately detect and track objects in real-time significantly contributes to safer and more efficient driving experiences.
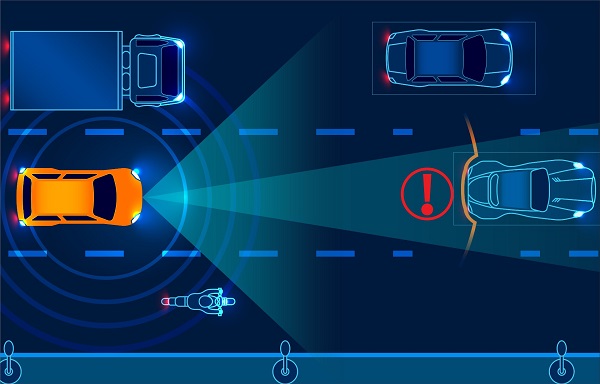
2 Image source – https://www.utmel.com/
-
Security and Surveillance:
MmWave radar can be used in security systems to monitor areas for unauthorized individuals. It can detect and track intruders in real-time, alerting security personnel to potential threats.

3 Image Source – https://www.minew.com/
-
Crowd Monitoring:
In public spaces like airports, train stations, or stadiums, mmWave radar can help monitor crowd movement and density. This information can be used for crowd control, safety planning, and optimizing space utilization.

4 Image Source – https://www.minew.com/
-
Meteorological:
Provides qualitative information about clouds’ presence, location, structure, turbulence, and dynamics. Its polarization capability allows for the analysis of cloud deformities, while integration with LIDAR enables the retrieval of clouds’ microphysical data. This combination of technologies enhances our understanding of cloud structures and dynamics, providing valuable insights for weather forecasting and atmospheric research.

5 Image Source – https://education.nationalgeographic.org/
-
Healthcare:
In healthcare, mmWave radar detects human gestures, heartbeats, breathing, and movements. This technology is applied in various applications such as blood pressure monitoring, emotional monitoring, and sleep tracking. The non-intrusive nature of mmWave radar allows for continuous monitoring without discomfort to the patient, making it a valuable tool in modern healthcare settings.

6- https://global.kyocera.com/be_innovation/medical-and-healthcare/interview1/
Conclusion:
With its ability to operate within the millimeter-wave frequency range, mmWave radar gives precise location, velocity, and angle with minimal interference. The versatility and reliability of millimeter-wave radar technology have made it indispensable across numerous industries. From enhancing automotive safety to improving meteorological forecasts and revolutionizing medical monitoring, millimeter-wave radar continues to push the boundaries of what is possible. As research and development in this field progresses, we can anticipate even more innovative applications that harness the full potential of this technology.


