Table of Content
Toggle1. Introduction
The EU MDR (Medical Device Regulation) is a new regulation that governs the production and distribution of medical devices in the European Union. It came into effect on May 25, 2021, and replaced the MDD (Medical Devices Directive) and AIMD (Active Implantable Medical Devices Directive).
The MDR introduces more stringent requirements for medical device manufacturers, including:
- A more robust quality management system (QMS)
- More rigorous clinical data requirements
- The appointment of a Person Responsible for Regulatory Compliance (PRRC)
- Increased scrutiny from notified bodies
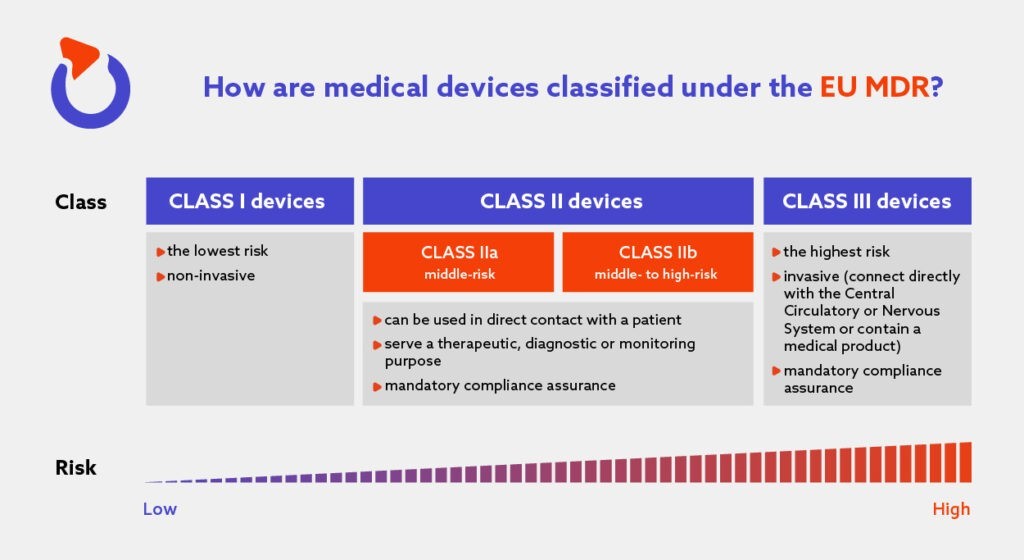
2. Classification of medical devices
Medical devices are classified into four classes based on the level of risk they pose to patients. Class I medical devices are the lowest-risk devices, while Class III medical devices are the highest-risk devices.
The MDR also introduces a new classification system for medical devices, with any software now classified as at least class IIa by default.
2.1 Class I medical devices
Class I medical devices are the lowest-risk devices and are typically used for general purposes. Examples of Class I medical devices include:
- Stethoscopes
- Tongue depressors
- Bandages
- Exam gloves
2.2 Class IIa medical devices
Class IIa medical devices are moderate-risk devices and are typically used for more specific purposes than Class I medical devices. Examples of Class IIa medical devices include:
- Blood pressure monitors
- Thermometers
- Glucose meters
- Nebulizers
2.3 Class IIb medical devices
Class IIb medical devices are moderate to high-risk devices and are typically used for more invasive or complex procedures than Class IIa medical devices. Examples of Class IIb medical devices include:
- Electrocardiogram (EKG) machines
- Ultrasound machines
- Surgical instruments
- Implantable devices
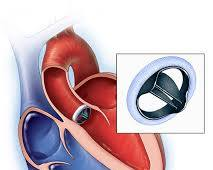
2.4 Class III medical devices
Class III medical devices are the highest-risk devices and are typically used for life-sustaining or life-threatening conditions. Examples of Class III medical devices include:
- Heart valve implants
- Pacemakers
- Cochlear implants
- Artificial joints
3. What does the MDR mean for medical device manufacturers?
The MDR means that medical device manufacturers need to make significant changes to their business processes in order to comply. This includes implementing a new QMS(Quality Management System), collecting more clinical data, and appointing a PRRC(Person Responsible for Regulatory Compliance).
3.1 Why is the MDR important?
The MDR is important because it is designed to improve the safety and quality of medical devices in the EU. By increasing the requirements for manufacturers, the MDR aims to reduce the risk of patients being harmed by defective medical devices.
4. What is ISO 13485?
ISO 13485 is an international standard that specifies requirements for a quality management system (QMS) for the design, development, production, installation, and servicing of medical devices. It is a voluntary standard, but it is widely accepted by medical device manufacturers around the world.
4.1 Why is ISO 13485 important?
ISO 13485 is important because it helps medical device manufacturers to ensure that their products are safe and effective. By following the requirements of ISO 13485, manufacturers can reduce the risk of errors and defects in their products.
4.2 How is ISO 13485 related to the EU MDR?
The EU MDR requires medical device manufacturers to have a QMS(Quality Management System) in place. ISO 13485 is a widely accepted QMS standard for medical device manufacturers. Therefore, complying with ISO 13485 can help manufacturers to comply with the EU MDR.
4.3 Benefits of ISO 13485 certification
There are several benefits to ISO 13485 certification, including:
- Improved product quality and safety
- Reduced risk of errors and defects
- Enhanced customer confidence
- Increased market access
- Reduced costs
4.4 How to get ISO 13485 certified?
To get ISO 13485 certified, manufacturers need to implement a QMS(Quality Management System) that meets the requirements of ISO 13485. Once the QMS is in place, the manufacturer needs to have their QMS audited by a certification body. If the audit is successful, the manufacturer will be awarded ISO 13485 certification.
5. What can medical device manufacturers do to prepare for the MDR?
Medical device manufacturers can prepare for the MDR by:
- Appointing a PRRC(Person Responsible for Regulatory Compliance) and classifying their devices
- Implementing a new QMS according to the MDR
- Preparing CE Technical Documentation per Annex II and III
- Appointing an Authorized Representative (EC REP) in the EU and obtaining a Single Registration Number (SRN)
- Undergoing Notified Body audit for non-Class I devices
- Receiving EC CE marking certificate for devices and ISO 13485 certificate for the facility
- Preparing a Declaration of Conformity (DoC) in accordance with Annex IV and affixing the CE marking
6. Conclusion
The EU MDR is a complex regulation that introduces significant changes for medical device manufacturers. However, it is important to note that the MDR is intended to improve the safety and quality of medical devices in the EU. By following the MDR certification process, manufacturers can ensure that their devices meet the highest standards and are safe for patients.
7. Additional tips for medical device manufacturers:
- Start planning for MDR compliance early. The MDR is a complex regulation, and it can take time to implement all of the required changes.
- Seek expert advice if needed. There are a number of consultants and organizations that can help medical device manufacturers comply with the MDR.
- Stay up-to-date with the latest MDR news and guidance. The European Commission publishes regular updates on the MDR website.
By following these tips, medical device manufacturers can increase their chances of success in complying with the MDR and bringing their products to market on time.
8. Abbreviations:
- Medical Device Regulation (MDR)
- Medical Devices Directive (MDD)
- Active Implantable Medical Devices Directive (AIMD)
- Quality Management System (QMS)
- Person Responsible for Compliance (PRRC)
- Notified Body
- Authorized Representative
- Consultation Procedure
- Unique Device Identification (UDI)
- EUDAMED
9. Website links:
- EU MDR website: https://health.ec.europa.eu/medical-devices-sector/overview_en
- EUDAMED website: https://webgate.ec.europa.eu/eudamed
- ISO 13485 website: https://www.iso.org/iso-13485-medical-devices.html